|
DOI: 10.25136/2409-7802.2017.2.21175
Дата направления статьи в редакцию:
22-11-2016
Дата публикации:
25-07-2017
Аннотация:
В настоящее время в России не происходит удовлетворение потребностей населения в овощных продуктах питания, потребление которых почти на половину меньше необходимых норм. Основными причинами являются низкий уровень производства овощей и покупательской способности населения, что в свою очередь связано с низким уровнем развития рыночной инфраструктуры. Это влечет настоятельную необходимость совершенствования инструментов агропродовольственной политики в отношении рынка овощной продукции, преобразования моделей организационно-экономического развития продовольственного рынка овощей. В работе использовались методы оценки рыночной концентрации Герфиндаля-Гиршмана, индекс Линда, методика анализа рыночного потенциала, экономико-математические методы экстраполяции трендов и оптимизации производства. Исследование выполнено по данным сельскохозяйственных товаропроизводителей овощной продукции Республики Мордовия. В работе показаны особенности и существующие проблемы эффективного функционирования овощного подкомплекса, обобщены основные факторы развития рынка овощной продукции, сформирована методика и проведены по ней анализ и оценка состояния конкурентной среды на рынке овощей в Республике Мордовия, разработаны модели по оптимизации структуры посевных площадей овощей в сельскохозяйственных предприятиях, по оценке рыночного потенциала овощеводческих предприятий, по организационной структуре оптового продовольственного рынка. Результаты исследования будут полезны органам власти для формирования продовольственной политики на рынке овощной продукции, так как позволяют определить перспективные направления и позиции в сфере сбыта овощной продукции, стимулирующие дальнейшее их производство.
Ключевые слова:
продовольственная политика, продовольственный рынок, рынок овощей, рыночная концентрация, рыночный потенциал, оптимизация производства, овощной подкомплекс, овощеводческие предприятия, овощи закрытого грунта, организационно-экономический механизм
УДК: 338.43
Исследование выполнено в рамках проекта РГНФ 16-32-00015 и при финансовой поддержки гранта Президента РФ МК-5177.2016.6
Abstract: Nowadays in Russia there is no satisfaction of needs of the population in vegetable products, which consumption is almost a half less than required standards. The main reasons are low level of vegetable production and the purchasing power of the population, which is associated with a low level of development of market infrastructure. The investigation was performed according to data about manufacturers of vegetable production of the Republic of Mordovia. In this article were used the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index, index Linda, technique of the analysis of market potential, economic-mathematical methods of extrapolation of trends and optimization of production. The necessity of improving the mechanisms of agrofood policy on market vegetables, showing characteristics and existing problems of effective functioning of vegetable subcomplex, summarizes the main factors of development of the market of vegetable production, formed the methodology and held on its analysis and assessment of the State of competition Wednesday at the vegetable market in the Republic of Mordovia, developed models to optimize the structure of sown areas under vegetables in agricultural enterprises, in the assessment of the market potential of vegetable growing on the organizational structure of the wholesale food market. Results of the study will be useful to the authorities for the formation of food policy on the vegetables market, because they allow to identify promising areas and positions in sales of vegetable products, that stimulate their further production.
Keywords: food policy, food market, vegetables market, market concentration, market potential, production optimization, vegetable subcomplex, vegerable-growing enterprises, vegetables of the closed soil, organizational and economic mechanism
Introduction In recent years, agriculture has become a national priority of State agricultural policy. The functioning of the agricultural sector is inextricably linked with the development of the food market that has a significant impact on the provision of population with food and improving food independence of the country. Among the most important directions of strategic development of agriculture to 2020 years was selected crop sub-sector development subprogram, the purpose of which is to ensure that indicators for the Doctrine of the Russian Federation in the field of food security crop products, including vegetables [1].
The market of vegetables is urged to provide a reliable supply of vegetables by creating the necessary conditions for stable development of business entities, their adaptation to market conditions, sustained growth of farmers incomes.
The vegetable market has social and economic importance, since through can solve tasks such as all-year and balanced provision of vegetables in sufficient quantity, assortment and quality of the processing industry with raw materials.
The vegetable market is the combination of socio-economic contacts between suppliers (producers) and buyers (demander), relating to the exchange, distribution and consumption of vital products to meet the growing needs of the population and strengthen his health, using inventory form [3].
The development of this subcomplex, until recently, was constrained by a number of economic reasons. Among them are the destruction of the logistics industry, the de-escalation of the price disparity, the domination of the market of monopoly and lack of healthy competition between the various manufacturers, and the lack of state influence on pricing processes. The structure of needs of the population was not enough connected with the structure of vegetable production, was the low level of marketing researches these needs and preferences, as well as forms of marketing of finished products.
During the period of the first state program (2008-2012) of domestic agriculture’s development took place in a complex and at the same time contradictory the socio-economic situation [9].
On the one hand, the country received further development of large agricultural formation, in the production of new technologies were introduced and technology, increased the number of adapted varieties and hybrids of crops, improved and expanded state support, formed a clearer system of State regulation of the food market and its individual product segments.
On the other hand, the changes have not provided the necessary reproductive opportunities in agriculture, largely preserved the systemic problems in its development. Still weak grew the investment opportunities in the industry, there were no significant positive changes in the formation of the innovation system and infrastructure of the agri-food market, slowly increased the demand for food products. The high price volatility for agricultural products was saved, with the steady increase in retail prices of foodstuffs [2].Results of a research The entered by Russia food embargo greatly affected the functioning and development of market of vegetable products. The business had to adapt to a fundamentally new socio-economic conditions at a fast pace.
In 2014, imports of fresh vegetables amounted to 2.18 million tons. The decline in imports of vegetables in 2014, compared with 2013, in real terms stands at 25 %. The reason for this sharp decrease in the annual indicator is the introduction of Russian food embargo. In August 2014, imports of vegetables fell by 44 %, in September by 51,5% in October, 50.6 %, November by 41% compared to the same periods of 2013.
According to the report of the Union of Mediterranean exporters of fresh fruit and vegetables, in January 2016, the export of fresh fruit and vegetables to Russia fell by 88% compared with January last year. As for only exporting fresh vegetables to Russia, the decline has exceeded 90%[10].
Russia plans to eliminate the deficit of vegetables in the market by increasing imports from China, Israel, Argentina, Iran, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. According to experts, it will lead to a deterioration of product quality.
Very high import dependence is observed in greenhouse horticulture. Consumption of greenhouse vegetables in Russia in 2014 amounted to 1.8 million tons, in which only 600 thousand tonnes of local production. Thus, imports account for about 67%, which are fresh vegetables that Russians consume from November to July (figure 1).
Today in Russia there are 1.8 thousand hectares of greenhouses, while in Poland 6.5 thousand hectares, of Holland – 11 thousand hectares, in Turkey – 35 thousand hectares To increase the market to 70% of greenhouse vegetables is necessary to increase the area of greenhouses in Russia to 4 thousand hectares.
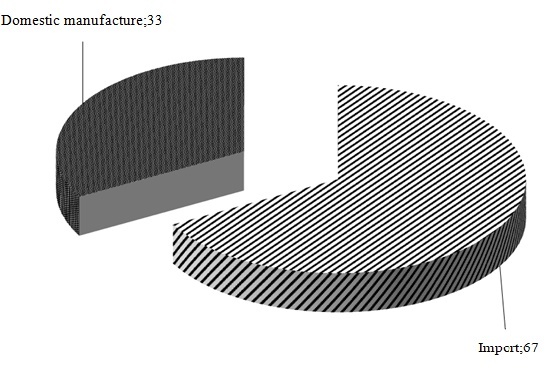
Figure 1 - Share of imports and domestic production in the vegetable-growing greenhouse
in 2014 %
In recent years, the level of actual intake of vegetables haven’t been according evidence-based norms. One resident of Russia consumes 100 kg of vegetables of domestic production, and medical standards required of 140-160 kg. Consumption of greenhouse vegetables of one men in Russia in year is 4.4 kg, and the norm should be 12-15 kg. Thus, the country does not provide domestic needs with its own production. Among the limiting factors significant role is played by underdevelopment of the market of vegetable production at the level of almost all its units starting from production to the final sale of vegetable products. All this is the main reasons for the increased cost of domestic vegetable production, reducing its competitiveness and continued high dependence on imports, especially in the big cities and large industrial centers [11].
The process of formation and functioning of the vegetable market is faced with disequilibriums that are reflected in the absence all-year the sale of vegetables, due to underproduction and underdeveloped this infrastructure [4].
The formation of the country's vegetable market associated with the introduction of contractual prices for vegetable products and the possibility of realization of the manufactured products in the market. However, in assessing transition vegetable farms in qualitatively new State should be recognized that the harnessing of certain market-based instruments in the absence of the indispensable conditions and without complex legal, economic and institutional measures won't lead to the emergence of well-functioning market [5, 6].
It should be noted that the vegetable market as part of a single food market is under the influence of complex factors that influence on the process of its formation and further development (Figure 2). 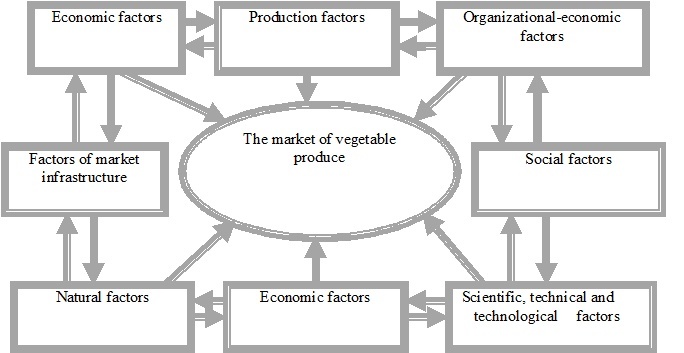
Figure 2- Factors of formation and development of the market of vegetable production
Development of the market depends on the diversity of this structure by types of vegetable production, where stand out specialized sales (cabbage, carrots, cucumbers, tomatoes, onions, beet, etc.), which is continually replenished with the growing needs of the population, as well as there is in their sales at central markets.
Considering the multi-criteria approach to the vegetable market on the scale of the functioning there are world, national, regional and local markets; according to the degree of restriction of competition there are perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly; according to the organization of market exchange there are wholesale and retail. Structure of members of the market is determined by diverse forms of ownership and types of management. Market members are:
-manufacturers of vegetable production (agricultural holdings, joint stock companies, partnership associations farmers' cooperatives, farmers ' and personal subsidiary farms of the population);
- national, mutual, trading and purchasing enterprises and their associations, consumer co-operations, individual entrepreneurs engaged in Commerce and procurement activities;
- Canned vegetables enterprise;
-national and commercial vegetable storehouses, warehousing;
-catering;
- industrial enterprises and associations that provide logistical resources;
- production infrastructure enterprises and organizations serving the industries of agroindustrial complex (industrial, agrochemical, transport, construction, etc.);
- economic formation of the market infrastructures (facilitating agency, auction and fairs system, banking, information and commercial centers, advertising services);
- integrated marketing formation type (farm firm, agrocomplex).
Therefore Vegetable market development remains a major strategic issue in Russia in general, and specifically in the Republic of Mordovia.
Analysis of grouping RM areas on total gathering of basic kinds of vegetables in the open field showed that the largest volume of production of vegetables is concentrated on the territory of Oktyabrsky district of the Republic of Moldova, where its activities have focused major manufacturers of vegetable products, in connection with which the area is selected as the main object of study.
Thus, the exchange of goods in the vegetable production is in several ways: through the old state custom distribution system; for direct links with consumers. However, in the structure of the implementation of the new stand out, including shadow, market structure that buy products in agricultural enterprises and supply it to the market to unjustifiably exorbitant prices. The diversity of channels implementation entails the price competition that predetermines the transformation of marketing of vegetable production. Sale of products through the consumer market is much more profitable, so this channel implementations continues to grow.
In order to clarify the essence of the market vegetable production was identified the degree of monopolization. The preliminary estimation of the degree of monopolization of the market, the uniformity or non-uniformity of presence on it as areas and businesses in the most concentrated area was held, the market share of each subject was determined and the values of concentration was calculated, which include the concentration ratio (CR) and Herfindahl-Hirschman Index(HHI). So, when evaluating the volume of commodity market resource through the Herfindahl-Hirschman’s Index over areas of the Republic of Mordovia (table 1), it was found that the greatest percentage (85.5%) in the market of manufacture of vegetable products of the Republic of Mordovia occupy the Oktyabr'sky district, which is the main supplier of vegetables for the city of Saransk.
Table 1 - Estimated indicators of the Herfindahl-Hirschman's Index over areas of the Republic of Mordovia
|
The name of the district
|
Sales, t
|
Market share,%
|
Squared part
|
|
Ardatovsky
|
45,2
|
0,26
|
0,0676
|
|
Bol’shebereznikovsky
|
41,1
|
0,24
|
0,0576
|
|
Krasnaia Sloboda
|
109,6
|
0,6
|
0,36
|
|
Lyambirsky
|
164,4
|
0,9
|
0,81
|
|
Romodanovsky
|
1947
|
11,3
|
127,69
|
|
Ruzayevsky
|
207,7
|
1,2
|
1,44
|
|
Oktyabr’sky
|
14 639,9
|
85,5
|
7 310,25
|
|
TOTAL
|
17 113,8
|
100
|
7 440,67
|
Using these activities studied regions, calculate the concentration ratio (CR).
Market of vegetable production that by areas of the Republic of Mordovia is deemed to high concentrated.
In addition to the concentration ratio and Herfindahl-Hirschman Index for characteristics of the studied market calculate is Lind's Index, which allows you to determine the degree of inequality between the leading product vendors on the market.
In the Oktyabr'sky district of three economic subject and personal subsidiary plot(PSP) produce vegetables. Provided that the region accounted for 85.5% of all production of field vegetables and 100% private for Saransk city, Lind's index must be calculated for these companies (table 2).
Table 2 - Estimated Lind's Index most major subjects over Oktyabr'sky area of the Republic of Mordovia
|
Business name
|
Implementation,t
|
Market share,%
|
|
1. SUE RM «Teplichny»
|
10 752,6
|
62,79
|
|
2. SUE RM «Luhovskoe»
|
1 703,3
|
9,94
|
|
3. LLC «Ovoshchprom»
|
1 184
|
6,91
|
|
4. PSP
|
1 000
|
5,86
|
In evaluating the percentage of an entity in the market realization of Saransk revealed that over 62% of the market occupies SUE RM «Teplichny». Oligopoly form the first two economic entity. From the theory of oligopoly is aware that if two or three firms dominate the market is a "loose" oligopoly. The SUE RM «Teplichny» and the SUE RM «Luhovskoe» are a two market leading subject.
At the next stage, an assessment of the market potential, which means the possibility of an entity have a decisive influence on the General conditions of treatment of the goods in the relevant market.
The main indicator of market potential is enterprise competitiveness index (or group of companies), he was defined in various ways, some scholars [8] define it as a piece of commodity competitiveness index mass delivered by the enterprise (Group of companies) to market, and production efficiency index. Index of enterprise's competitiveness must be supplemented by an index of the potential competitiveness of enterprise activities and production efficiency index divided by the index of efficiency of production activities and sales performance index.
Horticultural enterprises competitiveness assessment model was presented in the Figure 3. 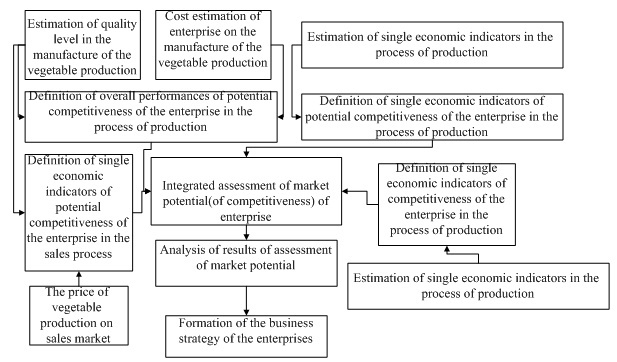 Figure 3 - Model for the assessment of the market potential of agricultural horticultural enterprises (without including PSP) Figure 3 - Model for the assessment of the market potential of agricultural horticultural enterprises (without including PSP)
Calculation of index of quality horticultural enterprises was realized a number of averages (arithmetic, harmonic and cubic). Results for the average of cubic and arithmetic mean coincided completely, and the arithmetic mean and the mean harmonic partially coincide, however, this mismatch does not play a significant role. Calculations on the proposed above are shown in the Table 3.
Table 3 - Indicators characterizing the market potential of the nuclear enterprises of the Oktyabr'sky area of the Republic of Mordovia.
|
Business name
|
Iп
|
Iпк
|
Im
|
Iэпд
|
Iэсд
|
|
SUE RM «Teplichny»
|
4,19
|
1,58
|
1,15
|
1,11
|
1,27
|
|
SUE RM «Luhovskoe»
|
3,76
|
1,69
|
1,01
|
1,04
|
1,04
|
|
LLC «Ovoshchprom»
|
2,57
|
0,60
|
0,96
|
1
|
1
|
Held a combined score more accurately, than existing, determine the level of competitiveness of horticultural enterprises, because in it uses a larger number of factors influencing it.
Thus, it was found that among the vegetable enterprises of the Oktyabr'sky area kastrychnitski district has the greatest potential of the SUE RM «Teplichny». This is because, in our view, the fact that this company has a favorable ratio of closed and open ground, enough high-quality products through the application of innovative and effective human resources strategy.
Implementation of the model for the optimization of production and competitiveness of enterprises to develop greenhouse and systematize the development trends of the market vegetables, including the formation of the wholesale market and the development of its infrastructure.
Implementation of the model for the optimization of production and competitiveness of enterprises to develop greenhouse and systematize the development trends of the market vegetables that including the formation of the wholesale market and the development of its infrastructure.
A model of the organizational structure of the wholesale food market of Saransk (Figure 4).
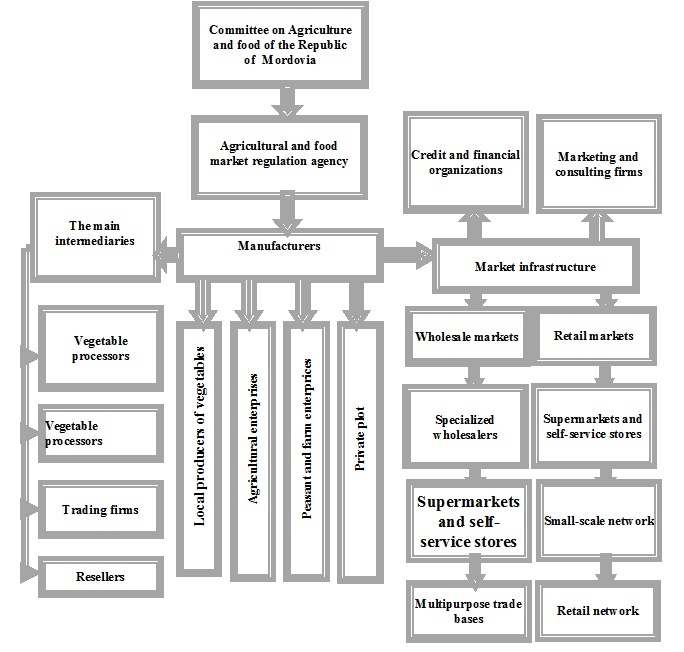
Figure 4 - The schematic model of organizational framework of the food market of the city Saransk of the Republic of Mordovia
This system of product distribution has several advantages:
- is carried out supply of big cities of fresh and high-quality food at affordable prices;
- agricultural commodity producers receive a guaranteed market for their products, when the wholesale market imposes certain requirements on manufacturers and suppliers of food in terms of the quality of the goods and their standardization, improve packaging and expansion of assortment;
- rise in the inventory turnover and formation of real market prices can increase profitability;
- market entity are provided with time-sensitive information on supply and demand, availability of goods, prices, when a separate problem is legal providing of forming and functioning of market of agricultural information, because the specific consists in certifying and giving to participants of the market process is free;
- the State can solve the problem of legalization of all financial flows and additional wholesale funds in the budgets of different levels, additional jobs are created.
General principles for the development of retail trade are presented in shaping the major universal retail enterprises, trading enterprises and complexes with a wide range of products sold primarily fresh vegetables.
Realization of economical relations between market participants vegetable production requires the strengthening of the institutional and economic instruments, the whole market mechanism (improving the competitiveness of enterprises, ordering, pricing, taking into account the demand and supply of products, development of entrepreneurial structures (agricultural holding), the development of large and small businesses and reducing natural manifestations of market). Conclusions Studies have shown that by providing the population with all-year vegetable products through commodity markets will require the creation of conditions for effective functioning of the market vegetable products:
- mapping results achieved production with current demand of market in vegetable production in accordance with its proposal on the market and taking into account the growth of incomes of the population;
- forming structurally-organized distribution system of production of vegetables in conjunction with the establishment of the appropriate infrastructure product market (specialized databases, vegetable stores, transport, spatial planning to host markets, trading places with the appropriate equipment for both legal entities and individuals (PSP, PFE) that engaging in wholesale and retail trade);
- create material prerequisites in the form of distribution networks to quickly promote the product from the manufacturer to the consumer with the least loss of quality and quantity of production;
- information support of participants of the market of vegetable products, which includes the establishment of a computer network with a data bank on regional market vegetables, collecting and processing information, dissemination of information on the availability of vegetables, current and projected prices, training participants the basics of agribusiness, marketing, stock trading;
- State regulation of the market of vegetable products that consisting in establishing targeted programmes of the AIC development for this industry. Regulation involves the interaction of complex administrative and organizational, legal and economic mechanisms. The impact of this interaction defines money solutions combining economic interests of three groups: consumers, producers and the State. Priorities should be given to consumers-purchasers of agricultural products, including vegetable;
- market exploration of vegetable production should be based on the results of complex marketing research that involving the analysis of the effectiveness of vegetable production as a source of trade resources for the regional market by type of crops and their purpose in ensuring a sustainable supply of all-year vegetables.
Thus, for sustainable and stable development of the market of vegetable products, it is advisable to pay serious attention to the development of market infrastructure for effective promotion of goods from producer to consumer, to create conditions for the integration of agriculture with the processing industry and trade.
The market mechanism unite all entities through relationships and connections that ensure the process of trade and exchange of agro-food resources in the commodity-money form.
The development of the market of vegetable production should be carried out to several competing against each other and complementary areas. The healing process and formation of market structures should also combine the continuity and gradual development the vegetable market.
One of perspective ways of development of the market of vegetable production is the formation of wholesale food markets. Wholesale market as self-regulating system is able to quickly establish a balance between supply and demand, where demand is a reflection of the population's income and purchasing power.
Organizational-economic mechanism of development of infrastructure of the wholesale food trade needs to develop towards an integrated approach to legal and tax regulation of the organization and integrated development of agricultural production, raw materials and food, wholesale trade, food processing industry, financial and credit sphere.
Библиография
1. Постановление Правительства РФ от 14.07.2012 N 717 (ред. от 15.04.2014) "О Государственной программе развития сельского хозяйства и регулирования рынков сельскохозяйственной продукции, сырья и продовольствия на 2013-2020 годы".
2. "Национальный доклад о ходе и результатах реализации в 2012 году Государственной программы развития сельского хозяйства и регулирования рынков сельскохозяйственной продукции, сырья и продовольствия на 2008-2012 годы" (утверждено распоряжением Правительства РФ от 08.05.2013 N 753-р).
3. Барышников Н.Г. Моделирование агропродовольственной политики региона / Н.Г. Барышников, Д.Ю. Самыгин // Экономика сельского хозяйства России. 2016. № 1. С. 71-76.
4. Барышников Н.Г., Самыгин Д.Ю., Дивненко З.А. Поиск новой модели стратегического развития агропродовольственного сектора // Сельское хозяйство. 2016. № 1. С. 19-26. DOI: 10.7256/2453-8809.2016.1.19537. URL: http://e-notabene.ru/sh/article_19537.html
5. Келейникова С.В. Система сбыта овощной продукции региона / С.В. Келейникова // Аграрная наука. 2007. № 2. С. 9-11.
6. Келейникова С.В. Моделирование продовольственной политики на рынке овощной продукции / С.В. Келейникова, Д.Ю. Самыгин, Н.А. Шлапакова // Аграрная Россия. 2014. № 11. С. 29-36.
7. Самыгин Д.Ю. Модели прогнозирования стратегического развития сельского хозяйства / Д.Ю. Самыгин, Н.Г. Барышников // Модели, системы, сети в экономике, технике, природе и обществе. 2015. № 1(13). С. 81-86.
8. Porter M.E. Competitive strategy. New York: The Free Press, 2004.416 p.
9. Samygin D.Yu., Baryshnikov N.G. Scenarios of Agricultural Business Development in Penza Oblast: Forecast and Risk Estimate // Studies on Russian Economic Development. 2015. Vol. 26. No. 1. pp. 59–62. DOI: 10.1134/S1075700715010037
10. Санкции России подорвали экспорт свежих овощей и фруктов // http://inosmi.ru/economic/20160224/235525638.html. Дата обращения 09.11.2016
11. Суслов Е.А. Развитие рынка овощной продукции в Российской Федерации: диссертация кандидата экономических наук: Всерос. науч.-исслед. ин-т экономики сел. хоз-ва РАСХН. М., 2010. 179 с.
12. Келейникова С.В. Кластерный подход как инструмент совершенствования управления отраслью овощеводства // Вестник Волжского университета им. В.Н. Татищева. 2014. № 1(30). С. 114.
13. Матвеева С.В. Экономическая конъюнктура России 1925-1926-х гг. и основные положения оптимизации развития экономики страны по Н.Д. Кондратьеву // Политика и Общество. 2014. № 7. C. 876-885. DOI: 10.7256/1812-8696.2014.7.12718.
14. Дойников И.В. Российская система хозяйствования: проблемы правовогорегулирования // Административное и муниципальное право. 2013. № 7. C. 731-742. DOI: 10.7256/1999-2807.2013.7.8925.
15. Тихонов А.А. Выбор модели стратегического управления развитием сельскохозяйственных предприятий // Тренды и управление. 2013. № 3. C. 82-90. DOI: 10.7256/2307-9118.2013.3.9402.
16. Рыжкова С.М. Современный рынок плодов и овощей в России: состояние и направления развития // Вестник Белгородского университета кооперации, экономики и права. 2016. № 1(57). С. 219-231
17. Родина Т.Е. Приоритетные направления формирования регионального рынка овощей // Международный научно-исследовательский журнал. 2016. № 6-1(48). С. 79-81.
18. Белокопытова Л.Е. Конъюнктура рынка - важный резерв роста экономики отрасли / Л.Е. Белокопытова, Г.Г. Крючков // Научное обозрение: теория и практика. 2016. № 9. С. 38-45.
References
1. Postanovlenie Pravitel'stva RF ot 14.07.2012 N 717 (red. ot 15.04.2014) "O Gosudarstvennoi programme razvitiya sel'skogo khozyaistva i regulirovaniya rynkov sel'skokhozyaistvennoi produktsii, syr'ya i prodovol'stviya na 2013-2020 gody".
2. "Natsional'nyi doklad o khode i rezul'tatakh realizatsii v 2012 godu Gosudarstvennoi programmy razvitiya sel'skogo khozyaistva i regulirovaniya rynkov sel'skokhozyaistvennoi produktsii, syr'ya i prodovol'stviya na 2008-2012 gody" (utverzhdeno rasporyazheniem Pravitel'stva RF ot 08.05.2013 N 753-r).
3. Baryshnikov N.G. Modelirovanie agroprodovol'stvennoi politiki regiona / N.G. Baryshnikov, D.Yu. Samygin // Ekonomika sel'skogo khozyaistva Rossii. 2016. № 1. S. 71-76.
4. Baryshnikov N.G., Samygin D.Yu., Divnenko Z.A. Poisk novoi modeli strategicheskogo razvitiya agroprodovol'stvennogo sektora // Sel'skoe khozyaistvo. 2016. № 1. S. 19-26. DOI: 10.7256/2453-8809.2016.1.19537. URL: http://e-notabene.ru/sh/article_19537.html
5. Keleinikova S.V. Sistema sbyta ovoshchnoi produktsii regiona / S.V. Keleinikova // Agrarnaya nauka. 2007. № 2. S. 9-11.
6. Keleinikova S.V. Modelirovanie prodovol'stvennoi politiki na rynke ovoshchnoi produktsii / S.V. Keleinikova, D.Yu. Samygin, N.A. Shlapakova // Agrarnaya Rossiya. 2014. № 11. S. 29-36.
7. Samygin D.Yu. Modeli prognozirovaniya strategicheskogo razvitiya sel'skogo khozyaistva / D.Yu. Samygin, N.G. Baryshnikov // Modeli, sistemy, seti v ekonomike, tekhnike, prirode i obshchestve. 2015. № 1(13). S. 81-86.
8. Porter M.E. Competitive strategy. New York: The Free Press, 2004.416 p.
9. Samygin D.Yu., Baryshnikov N.G. Scenarios of Agricultural Business Development in Penza Oblast: Forecast and Risk Estimate // Studies on Russian Economic Development. 2015. Vol. 26. No. 1. pp. 59–62. DOI: 10.1134/S1075700715010037
10. Sanktsii Rossii podorvali eksport svezhikh ovoshchei i fruktov // http://inosmi.ru/economic/20160224/235525638.html. Data obrashcheniya 09.11.2016
11. Suslov E.A. Razvitie rynka ovoshchnoi produktsii v Rossiiskoi Federatsii: dissertatsiya kandidata ekonomicheskikh nauk: Vseros. nauch.-issled. in-t ekonomiki sel. khoz-va RASKhN. M., 2010. 179 s.
12. Keleinikova S.V. Klasternyi podkhod kak instrument sovershenstvovaniya upravleniya otrasl'yu ovoshchevodstva // Vestnik Volzhskogo universiteta im. V.N. Tatishcheva. 2014. № 1(30). S. 114.
13. Matveeva S.V. Ekonomicheskaya kon''yunktura Rossii 1925-1926-kh gg. i osnovnye polozheniya optimizatsii razvitiya ekonomiki strany po N.D. Kondrat'evu // Politika i Obshchestvo. 2014. № 7. C. 876-885. DOI: 10.7256/1812-8696.2014.7.12718.
14. Doinikov I.V. Rossiiskaya sistema khozyaistvovaniya: problemy pravovogoregulirovaniya // Administrativnoe i munitsipal'noe pravo. 2013. № 7. C. 731-742. DOI: 10.7256/1999-2807.2013.7.8925.
15. Tikhonov A.A. Vybor modeli strategicheskogo upravleniya razvitiem sel'skokhozyaistvennykh predpriyatii // Trendy i upravlenie. 2013. № 3. C. 82-90. DOI: 10.7256/2307-9118.2013.3.9402.
16. Ryzhkova S.M. Sovremennyi rynok plodov i ovoshchei v Rossii: sostoyanie i napravleniya razvitiya // Vestnik Belgorodskogo universiteta kooperatsii, ekonomiki i prava. 2016. № 1(57). S. 219-231
17. Rodina T.E. Prioritetnye napravleniya formirovaniya regional'nogo rynka ovoshchei // Mezhdunarodnyi nauchno-issledovatel'skii zhurnal. 2016. № 6-1(48). S. 79-81.
18. Belokopytova L.E. Kon''yunktura rynka - vazhnyi rezerv rosta ekonomiki otrasli / L.E. Belokopytova, G.G. Kryuchkov // Nauchnoe obozrenie: teoriya i praktika. 2016. № 9. S. 38-45.
|


















 Статья опубликована с лицензией Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) – Лицензия «С указанием авторства – Некоммерческая».
Статья опубликована с лицензией Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) – Лицензия «С указанием авторства – Некоммерческая».
 Рус
Рус



